Nature publishes the largest "tree of life" of flowering plants to date
Escrito por UCC+iUCO researcher Manuel de la Estrella is part of an international team, led by the Kew Botanical Gardens, which has developed the "tree of life" of flowering plants as a tool with a multitude of uses, from the classification and identification of plants, to conservation in the face of climate change
A model estimates the cultivable space at photovoltaic plants, to combine agricultural and photovoltaic production
Escrito por UCC+iA team at the University of Cordoba has developed a methodology that defines the cultivable space between two-axis photovoltaic modules, with the aim of promoting the conversion of existing plants over to agrivoltaic production
A new 'Deep Learning' model predicts with great accuracy water and energy demands in Agriculture
Escrito por UCCiHydraulics and Irrigation researchers develop a model based on the ‘Transformer’ architecture to guide irrigation communities' decision-making
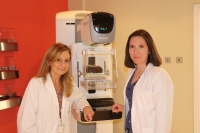
'3D mammography' almost halves the incidence of breast cancer between two screening tests
Escrito por UCC+iA clinical study in which almost 40,000 women have participated reveals the efficacy of breast tomosynthesis in decreasing the rate of interval carcinomas; that is, those that appear between two screening tests, suggesting the advisability of including this diagnostic technique in breast cancer early detection programs
The technological challenge of non-stick pans: Teflon is still more effective than other coatings
Escrito por UCC+iA protocol designed by the University of Cordoba yields a simple and robust evaluation of the efficiency and durability of different commercial non-stick coatings used for food preparation
A consortium of algae and bacteria boosts the production of green hydrogen and biomass while cleaning water
Escrito por UCC+iThe mutual relationship between an algae and three bacteria studied by a team at the University of Cordoba presents the highest hydrogen production obtained so far by this type of consortium